Random generation for the K distribution on df degrees of freedom having non-centrality parameter ncp.
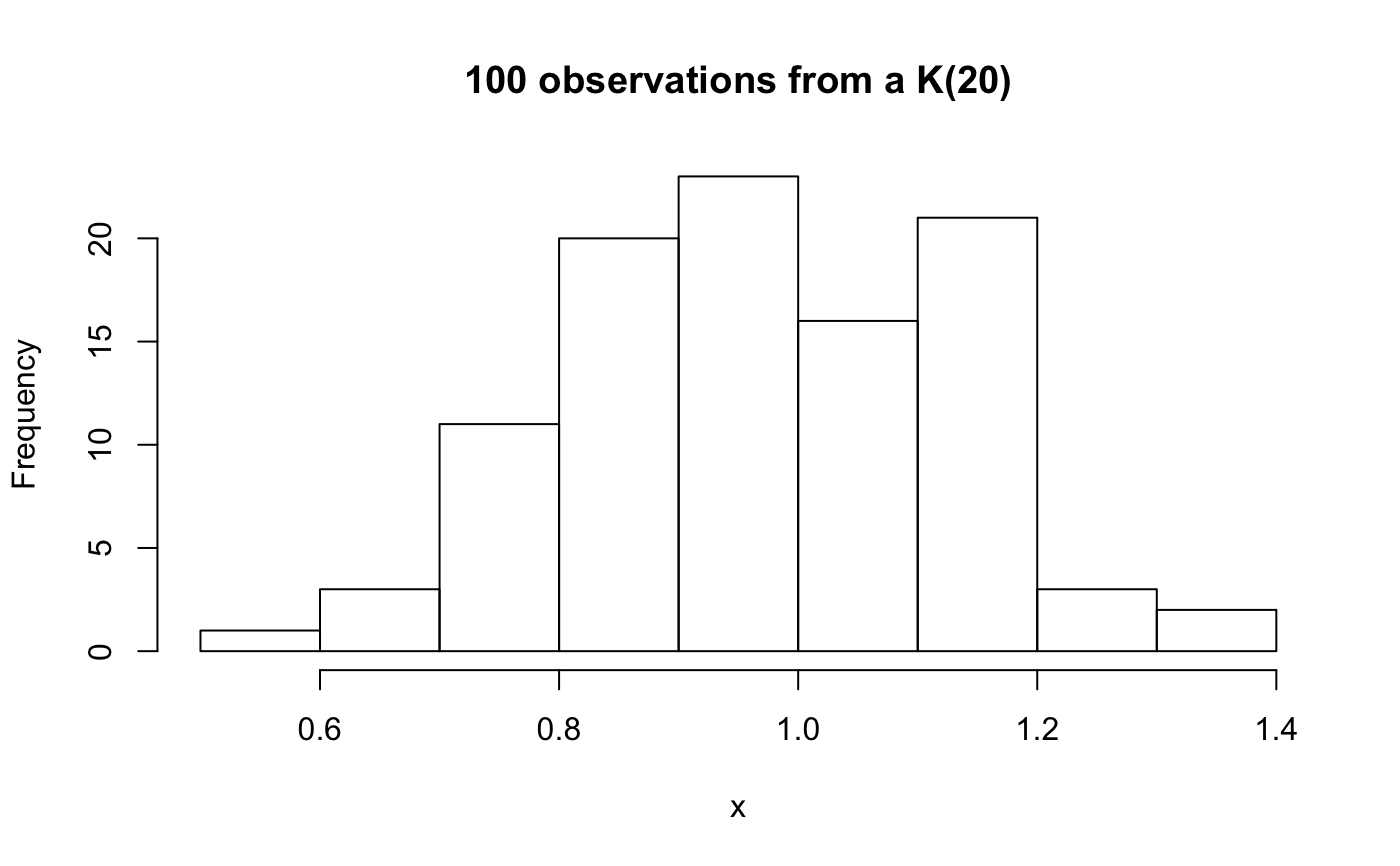
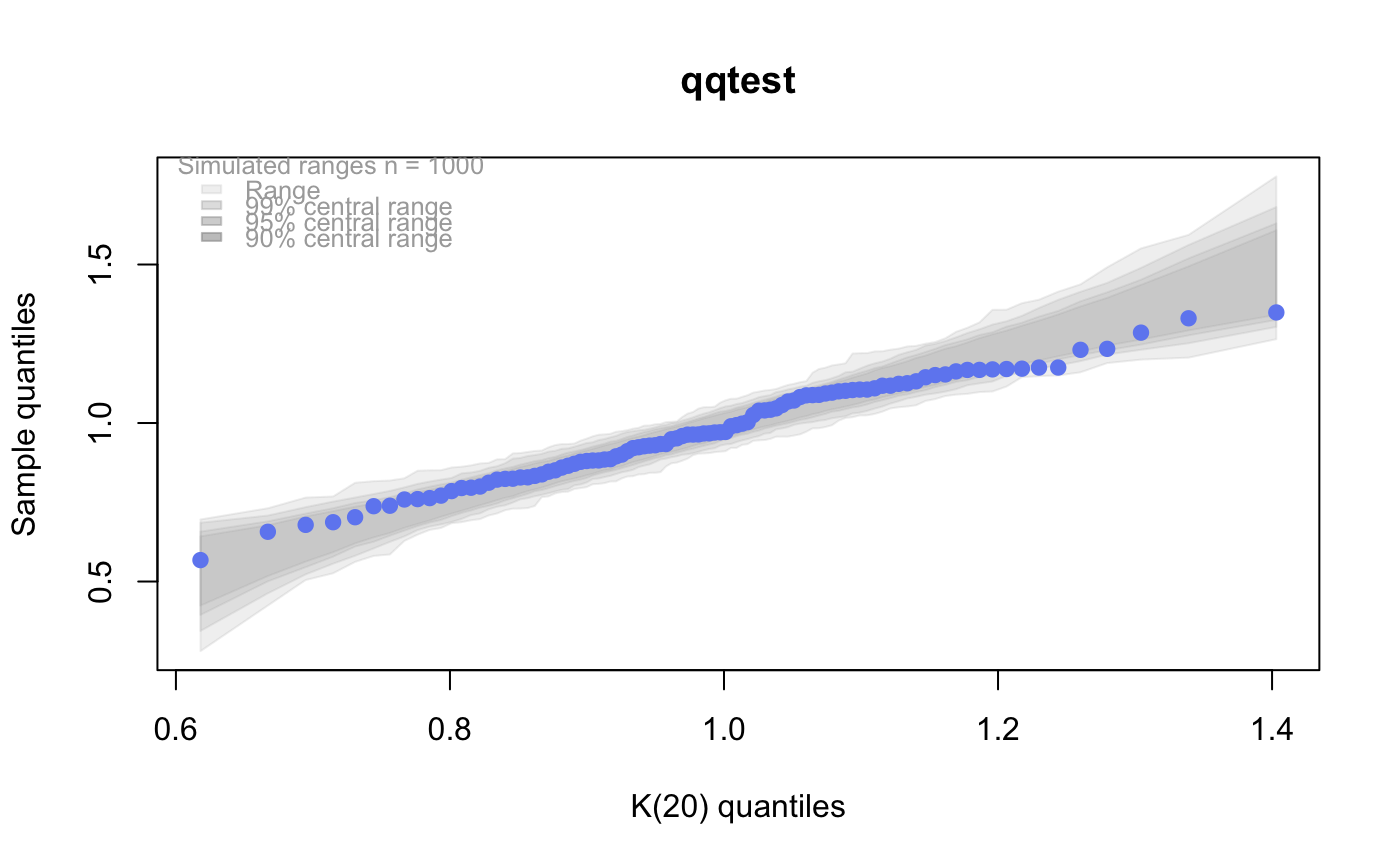
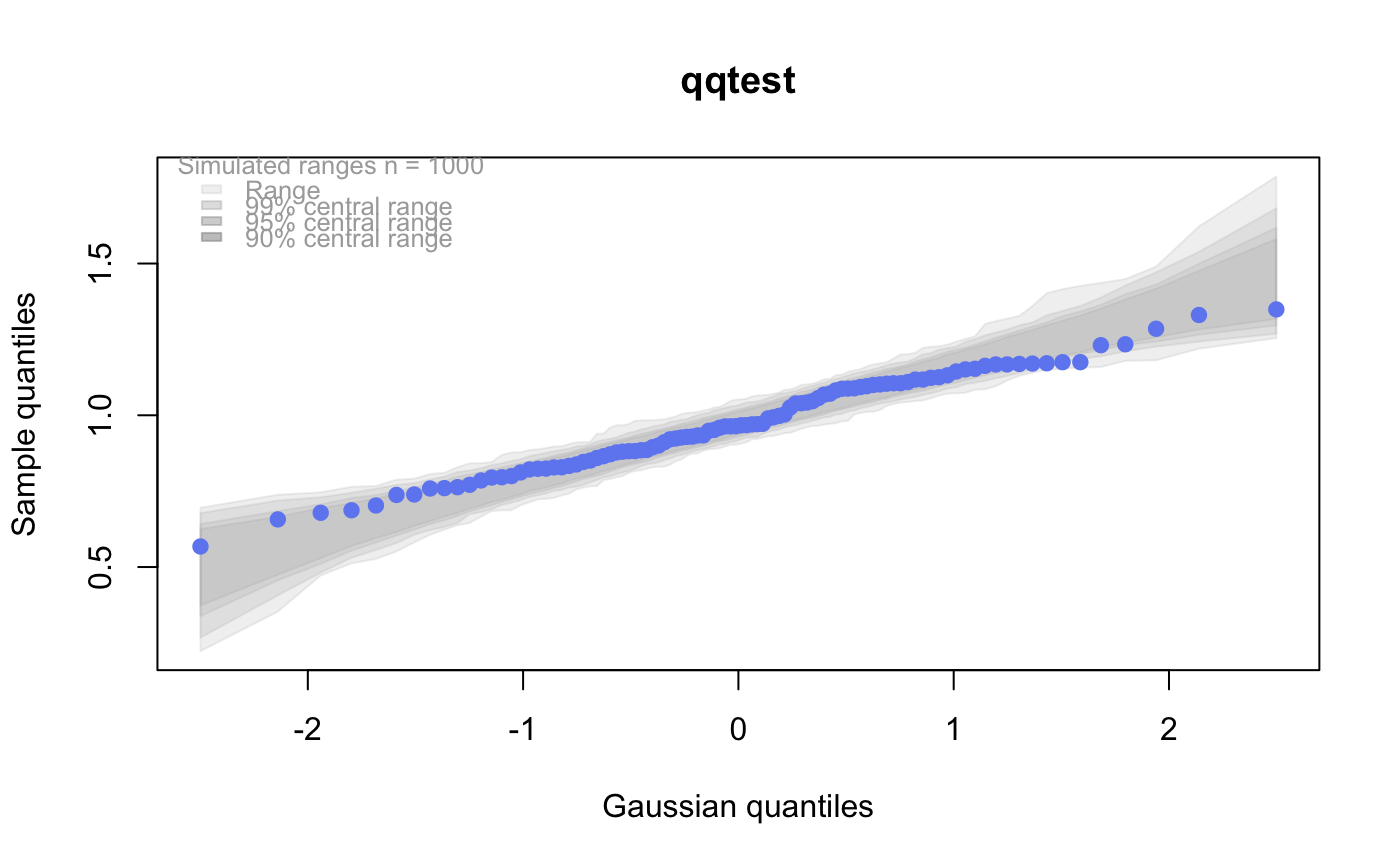
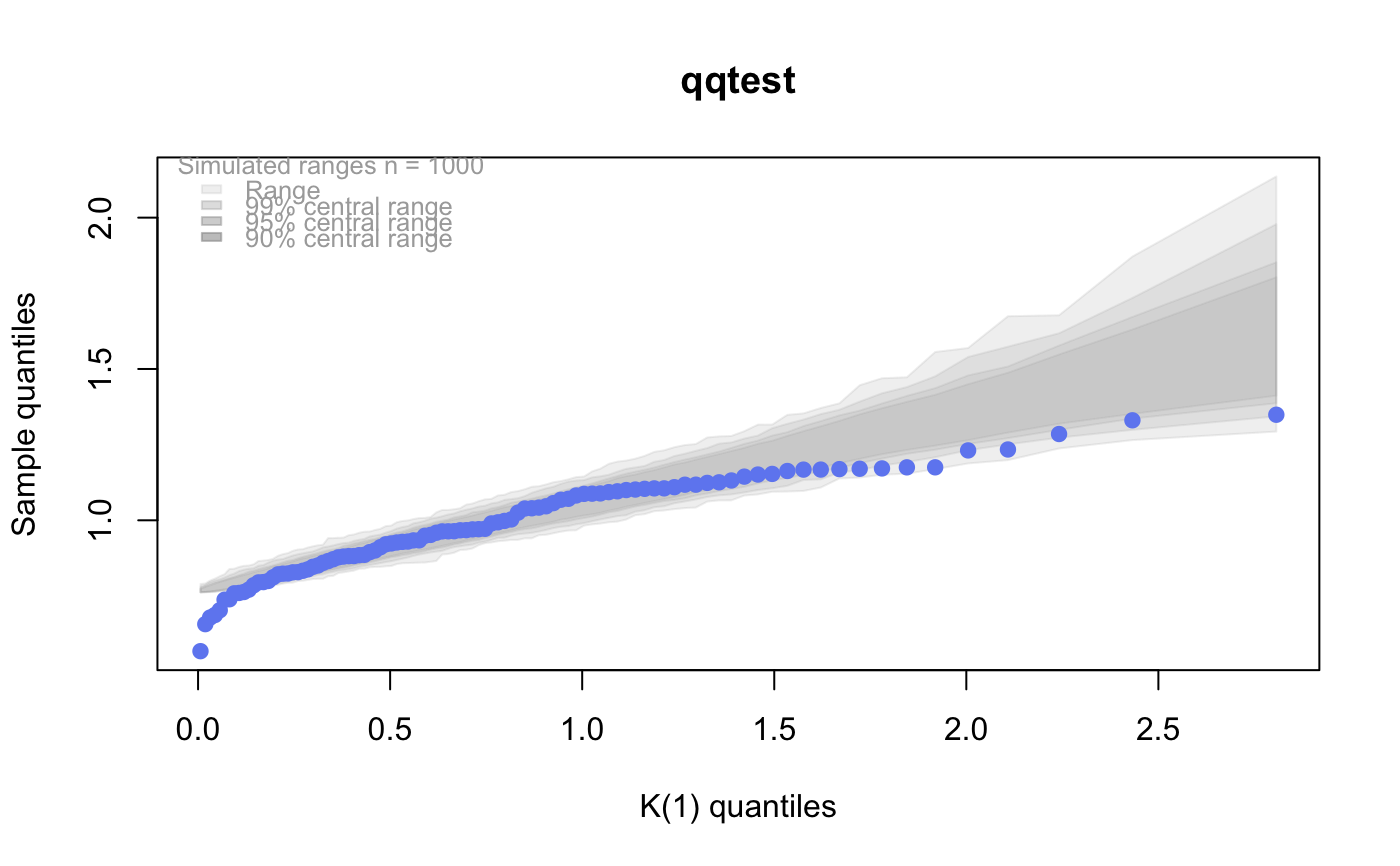
A K distribution is the square root of a chi-square divided by its degrees of freedom. That is, if x is chi-squared on m degrees of freedom, then y = sqrt(x/m) is K on m degrees of freedom. Under standard normal theory, K is the distribution of the pivotal quantity s/sigma where s is the sample standard deviation and sigma is the standard deviation parameter of the normal density. K is the natural distribution for tests and confidence intervals about sigma. K densities are more nearly symmetric than are chi-squared and concentrate near 1. As the degrees of freedom increase, they become more symmetric, more concentrated, and more nearly normally distributed.
rkay(n, df, ncp = 0)
Arguments
| n | Number of observations. If |
|---|---|
| df | Degrees of freedom (non-negative, but can be non-integer). |
| ncp | Non-centrality parameter (non-negative). |
Value
rkay returns pseudo-randomly generated values.
Invalid arguments will result in return value NaN, with a warning.
Note
Depends on call to analogous chi-squared functions. See rchisq for details on non-centrality parameter calculations.
Examples
# for this many degrees of freedom it looks # a lot like a gaussian (normal) distribution qqtest(x, dist="gau",df=1)# # See the vignette for more on the "K-distribution" #